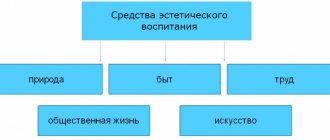
Features of children's design in a preschool institution and its role in raising children
Lecture No. 1
Topic : Constructive activities of preschool children.
Lecture outline:
1. Features of children's design in preschool organizations and its role in the development of preschool children.
2. Features of constructive activity of mentally retarded preschool children.
3. The main objectives of teaching construction to mentally retarded preschoolers.
4. Forms of organizing teaching design to preschoolers.
Literature:
1. Agayeva I.B. Theory and methods of teaching play, design and work to preschool children with intellectual disabilities / Reader. – Krasnoyarsk, 2009.
2. Gavrilushkina O.P., Sokolova N.D. Education and training of mentally retarded preschool children. – M., “Enlightenment”, 1985. P.7
3. Preschool education of abnormal children / Ed. L.P. Noskova. – M., “Enlightenment”, 1993. pp. 164-180.
4. Methods of teaching visual arts and design./ Ed. T.S. Komarova. – M., “Enlightenment”, 1991. P.198
5. Paramonova L.A. Theory and methodology of creative design in kindergarten. M., 2002. S. 5 – 28
Main:
1. Gavrilushkina Olga Petrovna. Design training in kindergarten for mentally retarded children. - M., 1991
2. Preschool education of abnormal children / Ed. Lyudmila Petrovna Noskova. - M., 1993
3. Ekzhanova Elena Anatolyevna, Strebeleva Elena Antonovna. Compensatory preschool educational program for children with intellectual disabilities. - M., 2003.
4. Paramonova Larisa Alekseevna. Theory and methodology of creative design in kindergarten. M., 2002.
Additional:
1. Gavrilushkina Oolga Petrovna, Sokolova Nadezhda Dmitrievna. Education and training of mentally retarded preschool children. – M., 1985.
2. Kosminskaya V.V., Vasilyeva E.I. and others. Theory and methodology of visual activity in kindergarten. - M., 1977. S. 190 - 203.
3. Lishtvan Zinaida Vasilievna. Construction. - M., 1981
4. Methods of teaching visual arts and design / Ed. Komarova Tamara Semenovna. - M., 1991. S. 198 - 222.
Features of children's design in a preschool institution and its role in raising children
Construction (from Latin construere ) means bringing various objects, parts, elements into a certain relative position.
Children's design is usually understood as the creation of various structures and models from building materials and construction parts, the production of crafts and toys from paper, cardboard, various natural materials (moss, branches, pine cones, stones, etc.) and waste materials (cardboard boxes, wooden coils, rubber tires, old metal things, etc.) material.
There are two types of design:
Ø technical
Ø artistic.
In technical design, children mainly display real-life objects, and also come up with designs by association with images from fairy tales and films. At the same time, they model their main structural and functional features: a building with a roof, windows, a door, a ship with a deck, stern, steering wheel, etc.
The technical type of design activity includes:
Ø construction from building material
(wooden painted or unpainted parts of geometric shape);
Ø construction from construction parts
, having different methods of fastening;
Ø construction from large-sized modular blocks.
In artistic design, children create images that not only reflect their structure, but also express their attitude towards them, convey their character, use the technique as a “violation” of proportions, as well as color, texture, shape: a cheerful clown, a thin simpleton wolf, a handsome prince, etc., which leads, in the words of Alexander Vladimirovich Zaporozhets, to the formation of unique emotional images"
The artistic type of design includes design from paper and from natural materials.
Computer design and design from waste material can be both technical and artistic in nature, which depends on the goal that the preschooler or the adult sets for himself (through a computer program)
By its nature, children's design is similar to visual activities and games, because they also reflect the surrounding reality. Children's buildings and crafts are used practically (in games, when decorating a Christmas tree, as a gift for mom, etc.).
We talked about how design is an activity. So, what is constructive activity?
Constructive activity
- this is a practical activity aimed at obtaining a specific, pre-conceived real product that corresponds to its functional purpose.
The type of material determines the type of design.
The building material - small (tabletop) and large - is a set of various geometric bodies (cube, cylinder, prism, etc.).
During the classes, a variety of small building materials are used.
During classes, there should be more material than is required for a given building (both in terms of elements and quantity) in order to teach children to select only the necessary parts that correspond to the plan.
When organizing children's constructive activities from building materials, the teacher uses a variety of small toys depicting people, animals, plants, vehicles, etc.
Preschool children, when creating objects in their environment, build not in general, but for a specific purpose: a house for a bunny, a bridge for cars and pedestrians, a castle for a princess, etc. The use of toys makes construction meaningful and contributes to the development of play activities.
It is most convenient to store building materials in special cabinets with compartments for each type of part: the material is always laid strictly according to the forms, so that children can quickly take any form they need. Laying out the material into forms makes the work easier and helps preschoolers quickly remember the names of these forms.
The next type of construction material
Designers. Children of senior preschool age use various construction sets outside of classes - wooden, plastic, metal and ceramic, with which they can create various structures that differ in the way they attach parts.
Under the guidance of a teacher in classes, children master new methods of connection (on pins, grooves), learn to create a variety of movable structures using pictures and drawings. Attention is drawn to the special development in children of the ability to connect parts, since the participation of small muscles of the hands is required, which is still imperfect in preschoolers.
The teacher first studies the assembly instructions himself, thinks through what he will explain in detail to the children, and what they will do themselves.
Sets of building materials and construction sets are given to children gradually as they master them under the guidance of a teacher.
Paper, natural and additional materials are used
Preschoolers are introduced to different types of paper: thick paper, table paper, writing paper, glossy paper, semi-paper and thin cardboard.
A variety of natural materials (cones, acorns, branches, seeds, grass, etc.) and the ease of their processing are widely used in working with preschoolers.
Natural material is prepared in a timely manner by the teacher and preschoolers, and supplies are replenished throughout the year. In summer and autumn, straw, cones, and seeds are collected. It is better not to collect dried natural material, because... this makes work difficult - it crumbles and splits.
Fruit seeds, thoroughly washed and dried, are collected at any time of the year. Each type of material is stored in a separate box or bag.
When creating crafts, additional materials are used: paper, cardboard, plasticine, wire, matches, glue - casein, synthetic, dextrin - and tools - a knife, scissors, an awl, a needle.
Children's construction is closely related to play activities. Children build buildings (garages for cars, houses for people, etc.) and play with them.
This served as the basis for most foreign researchers (Härmann Retter, Clarice Mening, Stuart Smith, Kenneth Rubin, Karl Fuson, M. Stanovich-Kastori, Emelyan Kamenov, Steve Miller, etc.), as well as a number of domestic ones ( Evgenia Aleksandrovna Flerina, Vera Grigorievna Nechaeva , Zinaida Vasilievna Lishtvan, Antonina Nikolaevna Davidchuk, etc.) classify construction as a type of children's game.
The features of play and construction convince us of the advisability of fundamentally separating these two types of activities and the need to abandon the term “construction games”, because games like this simply don't exist. Here we are dealing with either a role-playing game (which includes construction elements that contribute to the development of the game plot), or with full-fledged construction as an activity that uses toys and game elements that positively influence the construction process itself.
Let us consider the dynamics of the relationship between play and construction throughout the preschool period.
At an early age, design is merged with play, then play becomes an incentive for design, which begins to acquire independent meaning for children.
By older preschool age, the formed construction stimulates the development of plot play and itself acquires a plot character (the child creates several structures united by one plot).
There are two interconnected stages in the design:
§ creation of a plan
§ execution.
The idea consists of thinking, planning, presenting the final result, and determining the methods and sequence of achieving it.
A number of domestic scientists ( Danil Borisovich Elkonin, Yuri Aleksandrovich Poluyanov, Leonid Abramovich Wenger, etc.) believe that only by the senior preschool age can a child move from an idea to its implementation.
Other researchers (Nikolai Nikolaevich Poddyakov, Antonina Nikolaevna Davidchuk, Larisa Alekseevna Paramonova, etc.) show that if children are purposefully taught, then at 4 years old preschoolers are able to move from idea to execution in their activities.
A feature of design thinking even among older schoolchildren is the combination and interaction of mental and practical acts (Toviy Vasilievich Kudryavtsev, Emilia Aleksandrovna Faraponova , etc.)
Practical activities can act as experimentation with the material. The idea is often clarified and changed as a result of exploratory practical actions, which is a positive moment for the further development of the design. Preschoolers often reason out loud, as if pronouncing their actions and their consequences.
All this happens only in the process of learning aimed at overcoming the following shortcomings of children's free
(without special training)
design
(Paramonova Larisa Alekseevna ) :
§ inaccuracy of the plan (explained by the unclear structure of the image);
§ instability of the design (children begin to create one object, but it turns out completely different and are content with that);
§ haste in performing activities and excessive enthusiasm for it (very little attention is paid to the plan);
§ unclear ideas about the sequence of actions and inability to plan them;
§ inability to analyze a problem in advance.
As many studies by Alexander Romanovich Luria, Larisa Alekseevna Paramonova, Zinaida Vasilievna Lishtvan, Vera Grigorievna Nechaeva and others have shown, children's design without overcoming these shortcomings proceeds at a very low level.
The source of children’s ideas is everything around them: the diverse objective and natural world, social phenomena, fiction, various types of activities, especially play. But preschoolers’ perception of the environment is often superficial: they grasp the external aspects of objects and phenomena. Therefore, it is important to create conditions for mastering the environment, to develop the ability to see the characteristic features of objects and phenomena, establish relationships between them and convey them in designs and crafts.
. In this case, construction is based on figurative ideas about real-life objects, which becomes the basis of children's plans.
The ability to operate with images in space (rotation, movement in space) is important. Mastering spatial thinking expands the capabilities of preschool children in various types of construction (from paper, construction kit parts, modules, etc.)
The emotional coloring of children's activities is significant
, which uses different materials to create images. The connection of construction with everyday life, with other types of activities (fine arts, games, theater, etc.) makes it interesting, emotional and is one of the means of self-expression.
Construction contributes to the comprehensive education of a preschooler. In the process of learning to design, the mental, moral, aesthetic and labor education of preschoolers is carried out, the ability to analyze objects in the surrounding world, independence of thinking, creativity, artistic taste is developed, personal qualities are formed (dedication, perseverance in achieving goals, the ability to establish business relationships, etc. ), which contributes to preparation for the transition to the next type of activity - educational.
That is, the designers make us into “my mother’s engineer”?
A)
Indian psychologists believe yes:
Underlined in red: “Passed by designers and reads engineering magazines—techie!”
- Thanks, Cap! (screen from the book General Psychology, 2003) B)
The Soviet teacher Makarenko thought similarly: “Play in a child’s life has the same meaning as activity, work, service in an adult. As a child is at play, so in many ways he will be at work when he grows up.” Sounds logical, but...
C) Actually, we don't know.
And just for fun, we conducted a mini-research at our place. About a third of the employees were interviewed. Half are developers and system administrators (20 people), half are managers, marketing, designers, lawyers and accounting (20 people).
Four questions were asked. Two in the questionnaire were mandatory. Above are the answers to the first required question.
Here are the answers to the second mandatory question:
Let's move on to the breakdown of “techies” and “non-techies”.
In the “technical” group, 16 people often played with construction sets as children. Ten are sure that this influenced their choice of profession (“I started with construction sets, then began assembling computers, websites, etc.”); three are sure that it was not. The rest are undecided.
In the “non-technical” group, designers loved almost the same in childhood - 15 people. Five see the connection: “I started with construction sets, began to assemble computers, websites, etc.” are designers and project managers. Seven do not see a connection between their choice of profession and their childhood hobbies.
G)
I wonder, do you feel a connection between what you played as a child and who you have become? Please tell us - mini-survey at the end of the post.
What to do when you grow up
Construction sets are useful for children.
Sometimes it even affects their future. What to do if you lack design skills after 18? We have collected several tips that have been tested by ourselves, time and Giktayms. Play with children.
This is a pain-free way to try out a bunch of construction kits. By the way, they say that construction is a good prevention of Alzheimer’s disease.
Start a hobby.
Apple engineer Andrew Carroll made a working copy of the Antikythera Mechanism using Lego.
And you can’t say that you wasted your time.
Make a business.
This is an excellent design option with unpredictable results. You can even make your own construction set and sell it.
If you stay in the small business niche, we have come up with a website builder for you.
Design websites.
The good thing about this option is that with the current level of technology development it is suitable for many - knowing HTML is no longer necessary.
Start Arduino.
This method is described on Giktayms on average once a day.
Be nostalgic.
When we did a survey within the company, people recalled how they kept and passed on children’s construction sets, made things out of sticks and ropes, and... how “every thing, after disassembling, turned into a construction set.”