Professional competence of a teacher is the key to the success of every child
Abstract: The article examines the totality of professional and personal qualities necessary for successful teaching activities.
The professionalism of a teacher is understood as a systemic integral characteristic of a personality, which is the relationship of pedagogical competence, pedagogical skill, professionally significant qualities and the individual image of a teacher, which determine the individuality of each professional teacher, ensuring the effectiveness and optimality of teaching activities.
There are many professions on earth, but there is only one calling. How often do we see people who go to work reluctantly? But does their disinterest in their role as an employee of a certain institution speak about their professionalism? The question is controversial. What if this person is a teacher going to work to count the minutes until the end of his shift? It’s scary to imagine how we would leave our baby to such an “unprofessional”…. But what kind of person can we consider a professional?
A teacher’s professionalism is a systemic integral characteristic of a person, representing the relationship between pedagogical competence, pedagogical skill, professionally significant qualities and the individual image of a teacher, which determine the individuality of each professional teacher, ensuring the effectiveness and optimality of teaching activities. [4;p.119]
The Federal State Educational Standard for Preschool Education states that “teaching workers implementing the Preschool Program must have the basic competencies necessary to create conditions for the development of children.”
The professional competence of a teacher is a multifactorial phenomenon that includes a system of theoretical knowledge of a teacher and ways of applying it in specific pedagogical situations, the teacher’s value orientations, as well as integrative indicators of his culture (speech, communication style, attitude towards himself and his activities, towards related areas knowledge, etc.).
In accordance with the definition of the concept of “professional competence,” teachers must:
1. Own modern pedagogical technologies and apply them in professional activities.
2. Be ready to solve professional problems.
3. Be able to control your activities in accordance with accepted rules and regulations.
The modern education system requires educators to constantly improve their knowledge. One of the conditions for the professional growth of a teacher is self-educational work (review on the Internet; reading methodological, pedagogical, psychological literature; attending seminars, conferences, direct educational activities of colleagues; discussions, meetings, exchange of experience with colleagues; systematically taking advanced training courses; holding open classes for analysis by colleagues; study of IR technologies; communication with colleagues in preschool educational institutions, the city and on the Internet; participation in competitions on the Internet; posting your developments on websites on the Internet).
Based on modern requirements, we can determine the main ways to develop a teacher’s professional competence:
— work in methodological associations, creative groups;
— research, experimental activities;
— innovative activity, development of new pedagogical technologies;
— various forms of pedagogical support;
— active participation in pedagogical competitions, master classes;
— generalization of one’s own teaching experience.
But none of the listed methods will be effective if the teacher himself does not realize the need to improve his own professional competence.
To do this, it is necessary to create conditions in which the teacher independently realizes the need to improve the level of his own professional qualities.
Within the framework of the developed professional standard of pedagogical activity, competence is understood as a new formation of the subject of activity, formed in the process of professional training, which is a systemic manifestation of knowledge, skills, abilities and personal qualities, allowing one to successfully solve functional tasks that constitute the essence of professional activity.
In the dictionary of S.I. Ozhegov, the concept of “competent” is defined as “informed, authoritative in any field.” [5;p. 123]
Competence is “the expected and measurable achievements of an individual that determine what the individual will be able to do upon completion of the learning process; a generalized characteristic that determines a specialist’s readiness to use his full potential (knowledge, skills, experience and personal qualities) for successful activities in a certain professional field” [2, p. 111].
A necessary component of a person’s professionalism is professional competence.
The main components of a teacher’s professional competence include:
1. Intellectual and pedagogical competence – the ability to apply acquired knowledge, experience in professional activities for effective teaching and education, the teacher’s ability to innovative activities;
2. Information competence – the amount of information a teacher has about himself, students, parents, and colleagues.
3. Regulatory competence – a teacher’s ability to manage his behavior, control his emotions, the ability to reflect, and stress resistance.
4. Communicative competence is a significant professional quality, including speech skills, listening skills, extraversion, and empathy.
5. The ability to communicate correctly with parents of students is one of the main and can be difficult skills. competencies.
Professional competence of a teacher is the ability to successfully act on the basis of practical experience, skills and knowledge in solving professional problems:
1. Knowledge of the specifics of preschool education and the peculiarities of organizing educational activities with children: base your work on the regulatory framework:
— Federal Law “On Education in the Russian Federation” No. 273-FZ of December 29, 2012;
— Order of the Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation dated October 17, 2013. No. 1155 “on approval of the federal state educational standard for preschool education”
— Methodological recommendations for preschool educational institutions on the preparation of educational educational programs based on the Federal State Educational Standard for Educational Education and an approximate educational educational program.
— Organization of the RPPS in accordance with the Federal State Educational Standard of Education.
In connection with the introduction of the Federal State Educational Standard, the way of organizing children's activities is changing: not the guidance of an adult, but the joint activity of an adult and a child in childhood.
Features of organizing partnership activities between an adult and children:
- Involvement of the teacher in activities on an equal basis with the children.
- Voluntary participation of children in activities (without psychological and disciplinary coercion).
- Free communication and movement of children during activities (subject to the organization of the workspace).
- Open time end of the lesson (everyone works at their own pace).
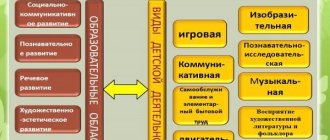
2. Knowledge of the patterns of child development (age-related characteristics), features of the formation and development of children's activities (in accordance with the Federal State Educational Standard for Education there are nine of them):
- Gaming activities (including role-playing games, games with rules and other types of games);
- Communication activities (communication and interaction with adults and peers);
- Cognitive and research activities (studying objects of the surrounding world and experimenting with them);
- Perception of fiction and folklore;
- Self-service and basic household work (indoors and outdoors);
- Construction from different materials (construction set, paper, modules, natural material, etc.);
- Visual activities (drawing, modeling, applique);
- Musical activity (perception and understanding of the meaning of musical works, singing, musical-rhythmic movements, playing children's musical instruments);
- Motor activity (mastery of basic movements, forms of child activity).
3. The ability to organize leading types of activities (object-manipulative - at an early age and play - at preschool age);
4. The ability to organize joint (partnership) activities of preschoolers.
Features of organizing partnership activities between an adult and children:
- involvement of the teacher in activities on an equal basis with the children;
- voluntary participation of children in activities (without psychological and disciplinary coercion);
- free communication and movement of children during activities (subject to the organization of the workspace);
— an open time end to continuous educational activities (everyone works at their own pace).
5. The ability to organize independent activities of preschool children (necessary conditions: a properly organized developmental subject-spatial environment and possession of the necessary skills);
6. Knowledge of technologies, methods, means, forms of activity and conditions for their application.
7. The ability to design, implement and analyze the effectiveness and results of one’s activities in accordance with the Federal State Educational Standard for Education (Includes knowledge of methods and means of conducting pedagogical diagnostics, the results of which can be used to solve the following problems: individualization of education, optimization of work with a group).
8. Participation in creating a psychologically comfortable and safe educational environment, ensuring the safety of children’s lives, preserving and strengthening their health, supporting the child’s emotional well-being during their stay in an educational organization.
9. Knowledge of methods and means of psychological and pedagogical education of parents, the ability to build partnerships with them to solve educational problems (use of active forms and methods of interaction)
10. Proficiency in ICT – competencies necessary and sufficient for planning, implementation and evaluation of educational activities with children.
The use of ICTs makes it possible to make educational activities emotionally charged and attractive. Presentations arouse keen interest in the child and are an excellent visual aid and demonstration material.
Interactive equipment must be used when working with children, subject to unconditional compliance with restrictive and permissive norms and recommendations, observe the operating time of the equipment, be sure to use sets of eye exercises, and ventilate the room.
One of the most important factors for the success of teaching activities is the professionally significant qualities of a teacher, such as modesty, observation, hard work, dedication, perseverance, oratorical abilities, and wit. Particularly important qualities of a teacher’s personality include readiness for empathy, i.e., to understand the mental state of students, empathy and the need for social interaction. In addition, a professional teacher must be: balanced, have high mobility of the nervous system, moderate extroversion, sthenicity of emotions and emotional stability.
Even with little work experience (7 years), I can say with confidence that a teacher must be patient. Showing restraint and patience in any situation, finding individual ways to influence children, trying to understand children's actions - this is what a true professional can do. Equally important is the teacher’s ability to step into the child’s shoes and see the situation through his eyes. Each child is unique, each has his own character, his own habits. But a real teacher accepts each child as his own, tries to find an approach and reveal the potential of each child. Only in this case will the child succeed.
Pedagogical skill is the basis of a teacher’s professionalism. This is a synthesis of personal and professional qualities and personality traits that determine the high effectiveness of the pedagogical process. [4; p.101]
There is simply a skilled teacher who conducts training and education at the usual professional level, and there is a teacher who demonstrates pedagogical skill and achieves high results in his work. Many teachers, in addition to their skill, demonstrate pedagogical creativity and, with their findings, enrich the methods of teaching and education. Pedagogical innovative activities in a preschool institution are associated with the transformation and improvement of the educational process, with the introduction of new, stable elements. Currently, the scope of innovation activity no longer includes individual preschool institutions and innovative teachers; In almost every preschool institution, innovative transformations are becoming systemic. This means that the kindergarten provides society with professionals who will confidently pass on their knowledge to our children, positively influencing their development, education and training.
The professionalism of a kindergarten teacher is realized in his versatility. First of all, he is a creative person. Only he can make a magic spoon out of an ordinary spoon, make superhero food out of an ordinary potato, and turn an ordinary car into a super car. Only he turns every activity into an extraordinary journey full of adventure. A modern teacher can do everything: dance, sing, act on stage, he draws and embroiders perfectly.
Pedagogical tact is another important component of the concept of teacher professionalism. It is realized in the ability to find the most correct pedagogical technique in every situation that arises. This is the teacher’s ability to behave with children, the ability in each individual case to understand the state of the pupil, his interests, motives and to find the most effective measure of education.
A teacher is a role model for his students. The image of a teacher, his specific image - the idea of the students around him and their parents, formed on the basis of his appearance, habits, manner of speaking, mentality, actions - is an important criterion that characterizes the teacher as a professional. [1;p. 58].
When forming the image of a teacher, real qualities are closely intertwined with those attributed to him by others. Appearance helps the teacher attract attention, create a positive image, and show himself not only as a nice person, but also as an excellent teacher. And children look up to the one they like, with whom they spend the most time.
Returning to the dependence of a child’s success on the professionalism of the teacher, we can say with confidence: a teacher is the first teacher, after the mother, that children meet on their life path. [2;p.36]. This profession is very responsible! It is not enough to have natural sensitivity; it is necessary to have an innovative style of scientific and pedagogical thinking, a readiness to create new values and make creative decisions. This is one of those professions in which professionalism is vital, because the future is in its hands - our children.
The work of a teacher is daily and painstaking work. This profession is multifaceted, non-standard, and requires a creative approach, self-improvement and spiritual generosity. But the most important thing in this work is to love children. To love children with all your heart means to invest in them the kindness of your soul, care, sensitivity and responsiveness, tenderness and patience.
Bibliography:
- Order of the Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation (Ministry of Education and Science of Russia) dated July 20, 2011 No. 2151 Moscow “On approval of federal state requirements for the conditions for the implementation of the basic general educational program of preschool education” // Russian newspaper dated November 21, 2011.
- Bidenko V.I. Competence-based approach to the design of state educational standards for higher professional education (methodological and methodological issues): Methodological manual. Ed. 2nd. – M.: Research Center for Problems of Quality of Training of Specialists, 2005. – 114 p.
- Lapteva, I.D. On the issue of pedagogical competence / I.D. Lapteva //Pedagogical education and science. - 2007. - No. 4.-P.35-38.
- Oleshkov M.Yu., Uvarov V.M. Modern educational process: basic concepts and terms. - M: Sputnik+ Company, 2006. - 191 p.
- Explanatory dictionary of the Russian language: Ok. 100,000 words, terms and phraseological expressions / S. I. Ozhegov; Ed. prof. L. I. Skvortsova. — 28th edition, revised. - M.: World and Education, 2015.
Criteria for assessing the quality of a teacher’s work
To determine the level of professional activity of a teacher, special assessment criteria are used, including the following points:
- The effectiveness of the teacher’s activities, manifested in the achievements of children from his group. It includes the following:
- Personal achievements of pupils, which are characterized by higher performance compared to the previous period.
- Preservation and strengthening of the physical and mental health of pupils.
- Absence or reduction of missed classes, low morbidity rate in the group.
- Development of creative abilities of pupils.
- Teacher self-education:
- Participation in the methodological activities of preschool educational institutions.
- Generalization and presentation of your teaching experience.
- Publications in scientific, professional and other publications.
- Participation in competitions at various levels.
- Stable management and high quality of documentation.
- Innovation activities:
- Development and implementation of creative or social projects, proprietary programs, technologies, methods that help improve the quality of work of a preschool institution.
- Development and implementation of innovative programs.
- Effective organization of a safe subject-development environment in a group.
- Interaction with parents and guardians of pupils.
Assessment of the quality of professional activity of a senior preschool teacher is carried out according to the following criteria:
- The effectiveness of the methodologist:
- Achievement of higher levels of professionalism by preschool teachers compared to the previous assessment period.
- A variety of forms of methodological work to improve the professional qualifications of the educational and teaching staff of preschool educational institutions.
- Comprehensive development of teachers’ creative abilities.
- Self-organization and self-education:
- Effective participation in the methodological work of a preschool institution.
- Generalization and presentation of experience.
- Publications.
- Participation in competitions.
- Timeliness and quality of documentation:
- Innovative activity of a teacher.
- Development and implementation of various projects together with specialized preschool education specialists.
- Mastering and implementing federal state requirements in preschool educational institutions.
- Effective organization of a subject-development environment in the methodological classroom.
- Organization of interaction and variety of forms of work with parents.
The criteria for assessing the teaching and educational activities of kindergarten employees not only influence their perception as successful specialists, but also affect the level of remuneration. During certification, teachers and educators with a high level of professional assessment have a greater chance of receiving higher qualifications, and this means a significant increase in salary.