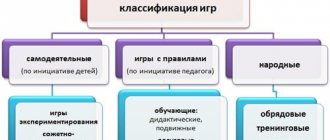
The importance of artistic and aesthetic development of preschool children
From early childhood, a child is drawn to bright, beautiful objects, so it is necessary to begin the artistic and aesthetic development of children from an early age. Children should act not only as contemplators and listeners, but also as active creators of beauty. Artistic and aesthetic education of the individual occurs from the first steps of a little person, from his first words and actions, and leaves an imprint on his soul for life.
Artistic and aesthetic education of preschoolers is a process as a result of which the child develops the ability to notice the beauty of the environment, love art and be involved in it. The word “beautiful” enters children’s lives early. From the first year of life, they hear a song, a fairy tale, look at pictures; simultaneously with reality, art becomes the source of their joyful experiences.
In the process of aesthetic education, they undergo a transition from an unconscious response to everything bright and beautiful to a conscious perception of beauty. The impact on the child’s personality must be targeted and systematic. The task of adults is to form the foundations of harmonious taste, develop the artistic and creative abilities of preschool children, their aesthetic feelings and ideas.
Preschool education consists of many artistic and aesthetic techniques. This includes inventing novels and stories, composing poems and songs, drawing and making decorative crafts. A naive and incredibly sincere reflection of actual reality, the absence of selfish motives, spontaneity and faith in everything said - this is what characterizes the artistic activity of preschool children. Already at this stage, there is a development of creative abilities, expressed in extraordinary imagination, the desire to bring a conceived idea to life, a skillful combination of one’s knowledge, skills and impressions received. The feelings, emotions and thoughts expressed are sincere and pure.
In the formation of artistic and aesthetic taste, the formation of children’s senses, familiarization of children with classic works of children’s fiction, musical works, and painting plays an important role.
The child is constantly creating and exploring something. All this is being improved and developed in creativity. Teachers of a preschool educational institution must help the child with artistic and aesthetic development so that he can develop comprehensively. Children receive their first artistic impressions, become familiar with art, and master various types of artistic activities, among which drawing, modeling, appliqué, and design occupy a large place.
Preschool age is the most favorable period for the development of a child’s creative abilities.
Being creative is also an acquaintance with folk culture
They are manifested in the ability to create a plan, develop a plot and find means to achieve a goal, implement a plan, combine acquired knowledge and one’s own ideas. This period is marked by incredible sincerity in the transmission of thoughts and emotions.
This is the musical and creative development of the child, education and training in ways and techniques of expressing ideas in drawing, music and words. Such development evokes in the child a conscious craving for everything beautiful, endows him with positive qualities, but also guarantees the unfolding of his potential. Quality education is not only about developing a child’s skills in musical performance, visual arts or other artistic and creative activities. It promotes independent work and the desire to improve oneself, fuels interest in the chosen form of art and arouses a desire to learn.
Another assistant in nurturing the artistic and aesthetic taste of preschoolers is native nature. The task of the teacher and parents is to see and show children drops of dew on the leaves of grass or on a cobweb, an interesting interweaving of grasses or the bright colors of a sunset... Works of art about nature will provide invaluable assistance in describing the beauty and charm of nature. It is important to be able to use all materials that preschoolers can understand. The child must understand the beauty of the surrounding nature
Architectural structures, streets, and buildings also represent an object for the moral, artistic and aesthetic education of children. During walks, children are shown the street with all its attractions. It is important to note some details and features of buildings, pay attention to individual shapes and lines, emphasize their feasibility and harmonious combination with other landscape objects.
The interaction between the teacher and parents guarantees the full development of the child’s abilities and the solution of problems of aesthetic education. Not every child will become a musician, writer or artist, but the knowledge gained will create conditions for raising a full-fledged citizen of his country, an exemplary family man and a morally formed person.
To receive the beginning of artistic and aesthetic education in childhood -
This means acquiring a sense of beauty for the rest of your life, the ability to understand and appreciate works of art, and to become involved in artistic creativity.
At the stage of preschool education, the goal of artistic and aesthetic education is to teach the child to see and understand the beauty around him.
From early childhood, a child is drawn to bright, beautiful objects, so it is necessary to begin the artistic and aesthetic development of children from an early age. Children should act not only as contemplators and listeners, but also as active creators of beauty. Artistic and aesthetic education of the individual occurs from the first steps of a little person, from his first words and actions, and leaves an imprint on his soul for life.
Psychologists and teachers have come to the conclusion that the early development of creativity, already in preschool childhood, is the key to future success. Children receive their first artistic impressions, become familiar with art, and master various types of artistic activities, among which drawing, modeling, appliqué, and design occupy a large place. Preschool age is the most favorable period for the development of a child’s creative abilities.
The child is constantly creating and exploring something. All this is being improved and developed in creativity. Teachers of a preschool educational institution must help the child with artistic and aesthetic development so that he can develop comprehensively. The teacher must lead the child from the perception of beauty,
In the formation of artistic and aesthetic taste, the formation of children’s senses, familiarization of children with classic works of children’s fiction, musical works, and painting plays an important role.
The use of modern technologies in the artistic and aesthetic development of preschool children.
Preschool age is the time when the foundations for the entire future development of humanity are laid. This is the most important stage in the development and education of the individual. This is a period of development of cognitive interest and curiosity, initial socialization, activation of independent thinking, and introduction of the child to knowledge of the world around him. In this regard, the education of preschoolers’ artistic taste, the formation of their creative skills, and their awareness of the sense of beauty is of particular relevance.
The artistic and aesthetic development of a preschooler is formed in the process of artistic and aesthetic activity through practical and emotional experience. This contributes to the development of such personality qualities as cognitive activity, emotional competence, independence, initiative, etc.
Based on the requirements of the Federal State Educational Standard for Preschool Education, the main tasks of the artistic and aesthetic development of a preschooler are:
- development of children's artistic creativity, interest in independent creative activities (visual, constructive-model, musical, etc.);
- satisfying children's needs for self-expression;
- the formation of interest in the aesthetic side of the surrounding reality, an aesthetic attitude towards objects and phenomena of the surrounding world, works of art;
- perception of music, fiction, folklore;
- development of children’s aesthetic feelings, artistic perception, figurative ideas, imagination, artistic and creative abilities;
- the formation of an aesthetic attitude towards the surrounding world.
The main means of solving these problems are modern pedagogical technologies (activity-type technologies), which make it possible to move to a qualitatively new level of training and education and contribute to the formation of a diversified, competent, creative, initiative personality of a preschool child. In modern pedagogical practice, there are many pedagogical technologies aimed at solving specific pedagogical problems.
In my work, I use such pedagogical technologies that help bring me, as a modern teacher, as close as possible to solving problems from the point of view of the artistic and aesthetic development of children:
- gaming technology
- research technology (experimentation)
- information and communication technologies;
- TRIZ technology ;
- technology of project activities.
The relevance of technologies for artistic and aesthetic development lies in the fact that they contribute to the development in children of:
- imaginative thinking;
- aesthetic perception;
- imagination, without which no artistic or creative activity is possible;
- emotional attitude to objects of an aesthetic nature;
- fine motor skills
Gaming technology
For preschoolers, the leading activity is play. Acquaintance with color and its properties begins in the game. Experimenting with material, mixing two or more colors, getting a new color for children is not an easy everyday thing, but a real miracle that happens here and now. It inspires children to seek new discoveries. Using colored pencils, wax crayons, and oil crayons, you can obtain new colors and shades by applying shading with the end of a pencil, chalk, or shading the crayons in two or three colors. Children develop interest in visual arts, creative imagination, and confidence in their own abilities.
We recommend: What should a 2-3 year old child be able to do?
Moreover, in my work I use such game techniques as a surprise moment (Droplet came to visit, “Blob the Mischief”, etc.), game situations ( “let’s help Bead find his color” ), which serve as motivation for active activities of the child, have a positive emotional response. Also, in fine arts classes, I actively use fairy-tale characters, games to develop the eye, correct a mistake, assemble a pattern, mix colors, etc.
Technology of research activities (experimentation)
Creative development begins with experimentation. Thanks to experimentation, children acquire such important qualities as creativity, independence, readiness for alternative solutions, the ability to reason logically, etc.
The experiment performs another important function - it allows the child to get rid of the fear of failure in his artistic searches.
Games with colors:
- Obtaining new shades by mixing paints.
- Use of different visual materials and imaging techniques.
- Mastery of various visual instruments.
- Creation of various visual materials.
The proposed games with colors help to introduce the preschooler to research, experimental activities, and the search for non-standard ways to solve problems. It should be noted that in the creative development of a child, the interaction between teacher and parent, parents and children is of great importance. In my practice, I use a variety of games with color, based on the optical properties of light perception, experiments with mixing colors, as well as various pigments and experiments with different materials.
ICT technologies
The modern pedagogical process has changed with the advent of the computer, an increase in the flow of information, cultural changes have occurred, and science is rapidly developing. This necessitates the reorientation of the teacher from the process of transferring ready-made knowledge to the process of creativity, the development of the individuality of each child, which is especially important in the preschool education system. In order to develop the creative abilities of preschoolers, the teacher himself must be a creative person and strive to master modern technological techniques. In the process of artistic and aesthetic development of a child, the ability for figurative, panoramic, multisensory perception of the world is formed, which plays a significant role in systemic thinking and creative decision-making. ICT helps improve the quality of the educational process and serves to develop the cognitive motivation of preschoolers. The positive side of this technology is that it allows you to increase the amount of illustration material, provides clarity, and allows you to quickly and better remember the material.
In my activities, I actively use ICT tools: a computer (music accompaniment, watching videos, presentations), as well as an interactive whiteboard. This allows me to ensure that the demo material is clear. Demonstration of presentations in visual arts classes helps to better convey the material through the use of a large number of illustrations. I also use a multimedia projector in my work, showing video material from virtual excursions to museums in the city and beyond. Learning for children becomes more fun and exciting, the material is better absorbed, causing positive emotions.
Technologies of project activities
The active use of design technology in the education and training of preschoolers and kindergartens allows you to get to know the preschooler better and penetrate into the child’s inner world. Children's project activities involve them completing collective, subgroup or individual projects together with the teacher and parents. Project activity allows you to combine different types of creativity when different artistic materials and techniques are combined. The participation of children and parents in experimenting and creating creative works contributes to the comprehensive development of the child, strengthening mutual understanding in the family, and creative manifestations not only in preschoolers, but also in their parents. At the beginning of the school year, I carried out the “Autumn Leaf” ; the project was designed not only for children, but for their parents. An event plan was developed, which included conversations, didactic and active games, organized thematic games during walks, an exhibition and a creative master class together with parents. This made it possible to update parent-child relationships, reveal the individual abilities of children, realize their interests and needs, which in turn made it possible to unleash the creative potential of all project participants.
TRIZ technology (the theory of solving inventive problems)
TRIZ methods and techniques cover many areas of educational activities. They did not ignore the visual arts either. There are methods and techniques that are firmly integrated into the structure of classes and planning of visual activities, enriching it with their diversity.
The goal of introducing TRIZ techniques into children's visual activities is to educate a creative, aesthetically developed personality capable of self-expression through various forms of visual activity.
Main goals:
- to cultivate the qualities of a creative personality;
- to develop creative work skills, including the following components: development of imagination, originality of thinking;
- develop the child’s ability to adapt to unexpected changes in the situation, the ability to reason and draw conclusions;
- develop resourcefulness, attentiveness and intelligence.
In my work, I use the following techniques of fantasy and development of creative imagination using non-traditional drawing techniques: blotography, monotype, drawing with threads, drops.
Association games, non-objective drawing on the topic: “Autumn is...” , “Spring is...” . I often use games of opposites, one object - different materials (discs, plasticine, waste and natural materials).
Thus, the use of TRIZ methods in a modern kindergarten can have a positive effect on the development of the qualities of a creative personality, productive imagination and visual skills of preschoolers.
To summarize all of the above, I would like to note that the use of modern technologies in the artistic and aesthetic development of preschool children not only contributes to the individual development of children, but is also an excellent means of developing a sustainable interest in experimental, research activities, and a creative search for solutions to non-standard problems.
Cultivating a sense of beauty is not limited to artistic and musical perception. This is a whole system that includes the child’s attitude to social work and life, to everyday life and nature.
But knowledge of art is the most valuable component of this multifaceted system, which helps to educate a child’s morality, develop musical and aesthetic feelings, imagination and fantasy.
The role of aesthetic education in child development
From the first days of life, a child is attracted to bright shiny toys and objects, colorful colors and attractive elements. Satisfied interest gives them a feeling of joy and pleasure. The concept of “beautiful” is recognized by the child very early. Listening to fairy tales or songs, looking at pictures and toys, they get a lot of positive emotions and experiences. These unconscious impulses, in the process of aesthetic education and development of preschool children, gradually transform into a conscious perception of beauty. The task of adults is to form the foundations of harmonious taste, develop the artistic and creative abilities of preschool children, their aesthetic feelings and ideas.
Understanding the world of art occurs through color, shape and sound. However, there are some features that determine the aesthetic education of preschoolers. It requires a highly developed sensory culture.
Introduction to beauty must begin from a very young age.
A child’s perception of beauty is inextricably linked with the ability to admire the form and content of an object. Form is a combination of colors, sounds and shapes. However, we have to talk about aesthetic education only when the perception of beauty is associated with an emotional component, with a personal attitude and empathy. Feelings are the basis of aesthetic education of preschool children. It is important to develop in a child the ability to rejoice unselfishly, to feel a light, bright excitement from meeting the beauty and charm of the world of art. It will take a lot of patience and strength from the teacher to unobtrusively instill in the child a love of beauty, which permeates his entire existence with noble motives and aspirations.
The emotional response and sensual aesthetic perception of beauty gradually moves to another level. This is the formation of one’s own judgments and ideas about the world of beauty.
Any creative activity is one of the methods of aesthetic education
Preschool education consists of many artistic and aesthetic techniques. This includes inventing novels and stories, composing poems and songs, drawing and making decorative crafts. A naive and incredibly sincere reflection of actual reality, the absence of selfish motives, spontaneity and faith in everything said - this is what characterizes the artistic activity of preschool children. Already at this stage, there is a development of creative abilities, expressed in extraordinary imagination, the desire to bring a conceived idea to life, a skillful combination of one’s knowledge, skills and impressions received. The feelings, emotions and thoughts expressed are sincere and pure.
MAGAZINE Preschooler.RF
The use of modern technologies in the artistic and aesthetic development of preschool children.Preschool age is the time when the foundations for the entire future development of humanity are laid. This is the most important stage in the development and education of the individual. This is a period of development of cognitive interest and curiosity, initial socialization, activation of independent thinking, and introduction of the child to knowledge of the world around him. In this regard, the education of preschoolers’ artistic taste, the formation of their creative skills, and their awareness of the sense of beauty is of particular relevance.
The artistic and aesthetic development of a preschooler is formed in the process of artistic and aesthetic activity through practical and emotional experience. This contributes to the development of such personality qualities as cognitive activity, emotional competence, independence, initiative, etc.
Based on the requirements of the Federal State Educational Standard for Preschool Education, the main tasks of the artistic and aesthetic development of a preschooler are:
- development of children's artistic creativity, interest in independent creative activities (visual, constructive-model, musical, etc.);
- satisfying children's needs for self-expression;
- the formation of interest in the aesthetic side of the surrounding reality, an aesthetic attitude towards objects and phenomena of the surrounding world, works of art;
- perception of music, fiction, folklore;
- development of children’s aesthetic feelings, artistic perception, figurative ideas, imagination, artistic and creative abilities;
- the formation of an aesthetic attitude towards the surrounding world.
The main means of solving these problems are modern pedagogical technologies (activity-type technologies), which make it possible to move to a qualitatively new level of training and education and contribute to the formation of a diversified, competent, creative, initiative personality of a preschool child. In modern pedagogical practice, there are many pedagogical technologies aimed at solving specific pedagogical problems.
In my work, I use such pedagogical technologies that help bring me, as a modern teacher, as close as possible to solving problems from the point of view of the artistic and aesthetic development of children:
- gaming technology
- research technology (experimentation)
- information and communication technologies;
- TRIZ technology ;
- technology of project activities.
The relevance of technologies for artistic and aesthetic development lies in the fact that they contribute to the development in children of:
- imaginative thinking;
- aesthetic perception;
- imagination, without which no artistic or creative activity is possible;
- emotional attitude to objects of an aesthetic nature;
- fine motor skills
Gaming technology
For preschoolers, the leading activity is play. Acquaintance with color and its properties begins in the game. Experimenting with material, mixing two or more colors, getting a new color for children is not an easy everyday thing, but a real miracle that happens here and now. It inspires children to seek new discoveries. Using colored pencils, wax crayons, and oil crayons, you can obtain new colors and shades by applying shading with the end of a pencil, chalk, or shading the crayons in two or three colors. Children develop interest in visual arts, creative imagination, and confidence in their own abilities.
Moreover, in my work I use such game techniques as a surprise moment (Droplet came to visit, “Blob the Mischief”, etc.), game situations ( “let’s help Bead find his color” ), which serve as motivation for active activities of the child, have a positive emotional response. Also, in fine arts classes, I actively use fairy-tale characters, games to develop the eye, correct a mistake, assemble a pattern, mix colors, etc.
Technology of research activities (experimentation)
Creative development begins with experimentation. Thanks to experimentation, children acquire such important qualities as creativity, independence, readiness for alternative solutions, the ability to reason logically, etc.
The experiment performs another important function - it allows the child to get rid of the fear of failure in his artistic searches.
Games with colors:
- Obtaining new shades by mixing paints.
- Use of different visual materials and imaging techniques.
- Mastery of various visual instruments.
- Creation of various visual materials.
The proposed games with colors help to introduce the preschooler to research, experimental activities, and the search for non-standard ways to solve problems. It should be noted that in the creative development of a child, the interaction between teacher and parent, parents and children is of great importance. In my practice, I use a variety of games with color, based on the optical properties of light perception, experiments with mixing colors, as well as various pigments and experiments with different materials.
ICT technologies
The modern pedagogical process has changed with the advent of the computer, an increase in the flow of information, cultural changes have occurred, and science is rapidly developing. This necessitates the reorientation of the teacher from the process of transferring ready-made knowledge to the process of creativity, the development of the individuality of each child, which is especially important in the preschool education system. In order to develop the creative abilities of preschoolers, the teacher himself must be a creative person and strive to master modern technological techniques. In the process of artistic and aesthetic development of a child, the ability for figurative, panoramic, multisensory perception of the world is formed, which plays a significant role in systemic thinking and creative decision-making. ICT helps improve the quality of the educational process and serves to develop the cognitive motivation of preschoolers. The positive side of this technology is that it allows you to increase the amount of illustration material, provides clarity, and allows you to quickly and better remember the material.
In my activities, I actively use ICT tools: a computer (music accompaniment, watching videos, presentations), as well as an interactive whiteboard. This allows me to ensure that the demo material is clear. Demonstration of presentations in visual arts classes helps to better convey the material through the use of a large number of illustrations. I also use a multimedia projector in my work, showing video material from virtual excursions to museums in the city and beyond. Learning for children becomes more fun and exciting, the material is better absorbed, causing positive emotions.
Technologies of project activities
The active use of design technology in the education and training of preschoolers and kindergartens allows you to get to know the preschooler better and penetrate into the child’s inner world. Children's project activities involve them completing collective, subgroup or individual projects together with the teacher and parents. Project activity allows you to combine different types of creativity when different artistic materials and techniques are combined. The participation of children and parents in experimenting and creating creative works contributes to the comprehensive development of the child, strengthening mutual understanding in the family, and creative manifestations not only in preschoolers, but also in their parents. At the beginning of the school year, I carried out the “Autumn Leaf” ; the project was designed not only for children, but for their parents. An event plan was developed, which included conversations, didactic and active games, organized thematic games during walks, an exhibition and a creative master class together with parents. This made it possible to update parent-child relationships, reveal the individual abilities of children, realize their interests and needs, which in turn made it possible to unleash the creative potential of all project participants.
TRIZ technology (the theory of solving inventive problems)
TRIZ methods and techniques cover many areas of educational activities. They did not ignore the visual arts either. There are methods and techniques that are firmly integrated into the structure of classes and planning of visual activities, enriching it with their diversity.
The goal of introducing TRIZ techniques into children's visual activities is to educate a creative, aesthetically developed personality capable of self-expression through various forms of visual activity.
Main goals:
- to cultivate the qualities of a creative personality;
- to develop creative work skills, including the following components: development of imagination, originality of thinking;
- develop the child’s ability to adapt to unexpected changes in the situation, the ability to reason and draw conclusions;
- develop resourcefulness, attentiveness and intelligence.
In my work, I use the following techniques of fantasy and development of creative imagination using non-traditional drawing techniques: blotography, monotype, drawing with threads, drops.
Association games, non-objective drawing on the topic: “Autumn is...” , “Spring is...” . I often use games of opposites, one object - different materials (discs, plasticine, waste and natural materials).
Thus, the use of TRIZ methods in a modern kindergarten can have a positive effect on the development of the qualities of a creative personality, productive imagination and visual skills of preschoolers.
To summarize all of the above, I would like to note that the use of modern technologies in the artistic and aesthetic development of preschool children not only contributes to the individual development of children, but is also an excellent means of developing a sustainable interest in experimental, research activities, and a creative search for solutions to non-standard problems.
| Next > |
“Modern technologies for the development of artistic and creative activities in preschool age”
Modern technologies for the development of artistic and creative activities in preschool age.
The joy of creativity is the most accessible
for a child, aesthetic spirituality.
V. A. Sukhomlinsky.
Preschool childhood is the most important stage in a child’s development. It is during this period that all the general abilities that an adult will need in any type of activity develop. Children's acquaintance with artistic creativity begins from preschool age - one of the methods recognized by modern psychology through the formation of personality and the development of its creative potential. It gives children joy, knowledge, and creativity. Artistic creativity is of great importance for the mental education of a child. In the process of artistic creativity, the stock of knowledge about the world around us gradually expands and assimilates. Based on ideas, children become familiar with materials (paper, paints, pencils, felt-tip pens, plasticine, clay, etc.), their properties and expressive capabilities. Introducing a child to the world of beauty reveals to children the richness and beauty of the surrounding life, contributes to the development of the need not only to contemplate the world, but also to actively understand and transform it. Mastering labor skills is associated with the development of such strong-willed personality traits as attention, perseverance, and endurance. Children develop the ability to work and develop a desire to achieve positive results. The main significance in artistic and creative activity is that it is an important means of aesthetic education, which gradually turns into ethical feelings that contribute to the formation of an aesthetic attitude to reality. The artistic and creative activity of preschoolers is of an emotional and creative nature. The teacher should create all conditions to ensure an emotional and imaginative perception of reality and ideas, the development of imaginative thinking and imagination.
V. A. Sukhomlinsky said that children should live in a world of beauty, games, fairy tales, music, drawing, fantasy, creativity, that his entire preschool path to knowledge.
Artistic and aesthetic development involves the development of prerequisites for holistic semantic perception and understanding of works of art (verbal, musical, visual), the natural world, the formation of an aesthetic attitude towards the surrounding world, the formation of elementary ideas in the arts, the implementation of independent activities of children (visual, constructive-model and etc.)
We watch with emotion the child drawing, trying to understand what he is drawing. Creativity reveals the child’s inner world, which is not always clear to others. Necessary components of creativity are the processes of thinking and imagination, therefore the development of creative abilities is possible only with the activation of these processes. Children try to express what they feel in their drawings. Psychologists, through children's creativity, are looking for an opportunity to penetrate into the unique inner world of a child. Therefore, visual activity is widely used for psychotherapeutic purposes. In the process of drawing, sculpting and applique, all types of memory develop, which helps to establish associations between the perception of reality and art, between different types of art, between previously perceived and present. Figurative memory is of particular importance in the process of visual activity, determining the necessary reserve of visual ideas in the drawing child.
Artistic and creative activities provide a great opportunity for children to demonstrate their creative activity. The topics of children's work are varied - children draw everything that interests them or the use of expressive means of drawing is available. Artistic and creative activities are aimed at achieving goals, developing interest in the aesthetic side of the surrounding reality, satisfying children's needs for self-expression through the development of productive activities, the development of children's creativity and familiarization with the fine arts. However, consciousness and mastery of the techniques of artistic and creative activity are quite difficult for a child. Therefore, we, teachers, must approach with great attention the formation of an aesthetic attitude towards the world in order to develop in each student the creative abilities inherent in nature. We must teach him to master the necessary methods of artistic and creative activity, to competently organize his artistic and aesthetic development. At a young preschool age, children strive for independence, become interested in others, become involved in fine arts, and gradually enter the world of beauty. The success of creative development largely depends on the adults who surround it: preschool teachers and parents. V. A. Sukhomlinsky Fr.
Current trends in the development of the sociocultural situation in the country are generating increasing interest in creativity in general and each person in particular. This is determined by the characteristics of the modern era. An important point is the possibility of developing the creative potential of each individual, that is, developing each person’s ability for active and conscious creativity, creative initiative, so that everyone can create, and not just reproduce.
Analyzing the development of abilities for visual activity in children, psychologist V.I. Kiriyenko writes: “For the vast majority of our subjects, the beginning of visual activity dates back to middle preschool age.” He emphasizes the need to study the early manifestation of ability.
By the senior preschool age, the child has formed the prerequisites for independent artistic and creative activity, which consists of the ability to create an original idea and embody it in his drawing, using all the variety of learned techniques and methods of representation. First of all, these are interests that gradually acquire a more pronounced social orientation under the conditions of upbringing. Artistic and creative abilities, abilities and skills should begin to be developed as early as possible, as this contributes to the development of artistic thinking, imagination, children’s memory, and observation. This should be done with proper guidance, taking into account the individual characteristics of preschoolers. When developing interest in artistic and creative activities, one should adhere to a personality-oriented approach to each child, support him, help him creatively perform work and evaluate his efforts. It is important to remember that it is in the process of artistic and creative activity that each child can show his or her individuality. Thus, teaching the techniques of artistic and creative activity can be a very real thing, which makes it possible to achieve the main goal - to give children the means of figurative expression, to give them the opportunity to experience the difficulties and joys associated with creative achievements.
Bibliography
- Boychuk I.A., Popushina T.N. Introducing children of primary preschool age to Russian folk art. - SPb.: CHILDREN'S PRESS, 2009
- Childhood: an approximate basic general education program for preschool education/ T.I. Babaeva, A.G. Gogoberidze, Z.A. Mikhailova and others - St. Petersburg: Detstvo-PRESS, 2011.
- Educational field “Artistic and aesthetic development” Methodological set of the “Childhood” program: educational methodological manual / scientific editor A.G. Gogoberidze. – St. Petersburg: LLC “PUBLISHING HOUSE” Detstvo-press; 2016.-400s
- Artistic creativity: comprehensive classes. First junior group/ O.V. Pavlova. Volgograd: Teacher, 2013.-142s
- Artistic and aesthetic development of children in the primary and secondary groups of preschool educational institutions. Long-term planning, notes. - St. Petersburg: LLC "PUBLISHING HOUSE" CHILDHOOD_PRESS", 2016, -320s
- Lykova I.A. Program for artistic education, training and development of children 2-7 years old “Colored palms”. M., 2007.
According to the PROGRAM “From birth to school”
According to the PROGRAM “From birth to school” - CyberPedia
| Single-post wooden support and methods for strengthening corner supports: Overhead line supports are structures designed to support wires at the required height above the ground, water... Transverse profiles of embankments and coastal strips: In urban areas, bank protection is designed taking into account technical and economic requirements, but special importance is given to aesthetic... |
Home Random page Feedback TOP Interesting to know Favorites
Top:
Integrated system for assessing the state of labor protection at a production facility (KSOT-P): Goals and objectives of the Integrated system for assessing the state of labor protection and identifying risk factors for labor protection...
Fundamentals of ensuring the uniformity of measurements: Ensuring the uniformity of measurements is the activity of metrological services aimed at achieving...
Theoretical significance of the work: A description of the theoretical significance (value) of the research results should be present in the introduction...
Interesting:
Reflection of the acquisition process in the accounting accounts: The procurement process represents a system of economic events, including the acquisition by an organization from suppliers of raw materials...
The influence of the business environment on the effective functioning of an enterprise: The business environment is a set of external and internal factors that influence the functioning of the company...
Treatment of advanced forms of cancer: One of the most important achievements of experimental tumor chemotherapy, begun in the 60s and implemented in the 70s, is...
Disciplines:
Automation Anthropology Archeology Architecture Audit Biology Accounting Military science Genetics Geography Geology Demography Journalism Zoology Foreign languages Computer science Art History Cinematography Computerization Shipbuilding Cooking Culture Lexicology Linguistics Literature Logic Marketing Mathematics Mechanical engineering Medicine Management Metallurgy Metrology Mechanics Musicology Science science Education Labor protection Pedagogy Political science Legal relations Entrepreneurship Instrument making Programming Production Industry Psychology Radio communications Religion Rhetoric Sociology Sports Standardization Statistics Construction Theology Technologies Trade Transport Pharmacology Physics Physiology Philosophy Finance Chemistry Economy Drawing Ecology Economics Electronics Energy Jurisprudence
| Page 1 of 3Next ⇒ PEDAGOGICAL DIAGNOSTICS level of preschool education According to the PROGRAM “From birth to school” Junior group PEDAGOGICAL DIAGNOSTICS “PHYSICAL DEVELOPMENT”. 2 JUNIOR GROUP. GEF DO The date of the: | |
| No. |
Last name, first name of the child
INDICATORS / MANIFESTATION Physical Culture HealthWalks straight, maintaining a given direction Runs, maintaining balance, changing direction, running pace in accordance with the task Maintains balance when walking on a limited plane, when stepping over objects Maintains balance when running on a limited plane (the plane is limited by lines on the floor) Crawls on all fours in an arbitrary manner Climbing a ladder in any way Climbs the gymnastic wall in any way Long jumps, pushing off with both legs Rolls the ball in a given direction Throws the ball with both hands from the chest Hit the ball on the floor 2-3 times and catches Throws the ball up 2-3 times and catches Throws objects into the distance Performs age-appropriate hygiene procedures independently (or after a reminder) adult) observes the basic rules of behavior while eating He himself (or after a reminder from an adult) observes the basic rules of behavior when washing himself Has a basic understanding of the value of health, the benefits of hardening, the need to observe hygiene rules in everyday life.1234 Efficiency of pedagogical influences %Legend:
Manifestation: not formed; is in the formative stage; formed
Note:
ü the indicator “formed” means that the indicator is stable, does not depend on the characteristics of the situation, the presence or absence of an adult, other children, the child’s mood, the success or failure of previous activities, etc.
ü the indicator “is at the stage of formation” means that the indicator periodically appears and its manifestation depends on the characteristics of the situation, the presence of control by an adult, the child’s mood, etc.
ü the indicator “not formed” means that the indicator appears extremely rarely and its appearance is random
Analytical report on the results of pedagogical diagnostics
in the educational field "Physical development"
Target:
— individualization of education for physical development (including support for the child, building his educational trajectory of his development);
— optimization of work with a group of children on physical development.
Methodology: when conducting pedagogical diagnostics, low-formalized methods were used: observation (in game situations, during regime moments, in directly organized activities)
Diagnostic results: the effectiveness of pedagogical actions was %, namely:
Physical Culture- %;
Formation of initial ideas about a healthy lifestyle - %.
Issues identified:
Causes:
Number of children with special educational needs:
Prospects for optimizing the physical development group:
Develop individual educational routes for the physical development of pupils:
Last name, first name of the child
INDICATORS / MANIFESTATION Labor education Target:— individualization of education for social and communicative development (including support for the child, building his educational trajectory of his development);
— optimization of work with a group of children on social and communicative development.
Methodology: when conducting pedagogical diagnostics, low-formalized methods were used: observation (in game situations, during regime moments, in directly organized activities)
Diagnostic results: the effectiveness of pedagogical actions was %, namely:
Socialization, development of communication, moral education – %. Child in the family and community - % Self-care, independence, labor education - % Formation of the foundations of safety - % Identified problems :
Causes:
Number of children with special educational needs:
Prospects for optimizing a group of children in terms of social and communicative development:
Develop individual educational routes for students:
Last name, first name of the child
INDICATORS / MANIFESTATION Musical activities Introduced to the arts Constructive modeling activities Target:— individualization of education for artistic and aesthetic development (including support for the child, building his educational trajectory of his development);
— optimization of work with a group of children on artistic and aesthetic development.
Methodology: when conducting pedagogical diagnostics, low-formalized methods were used: observation (in game situations, during regime moments, in directly organized activities)
Diagnostic results: the effectiveness of pedagogical actions was -%, namely:
Introduction to art - %. Visual activity - % Constructive-model activity - % Musical activity - % Identified problems :
Causes:
Number of children with special educational needs:
Prospects for optimizing the group for artistic and aesthetic development:
Develop individual educational routes for students:
Last name, first name of the child
INDICATORS / MANIFESTATION FEMP Social world Natural worldThe object environment examines objects, highlighting their color, size, shape; encourage to include hand movements on an object in the process of getting to know it Groups objects by color, size, shape, selects according to one characteristic With the help of an adult, makes groups of homogeneous objects and selects one object from the group (for example, collect all the large ones and find red among them Finds it in a familiar environment environment, several identical objects according to one characteristic Correctly determines the quantitative relationship of two groups of objects (understands the specific meaning of the words “more, less,” “the same”) Distinguishes between a circle, a square, a triangle, objects with corners and a round shape Understands the meaning of the designations: up and down , front-back, left-right, on, above, under Understands the meaning of words: morning, evening, day, night Knows his name, age, gender Interested in himself (Who am I?), information about himself, about the changes happening to him Orients himself in the room groups, on the site (veranda) of the group Names unfamiliar objects, explains their purpose, signs (color, shape, material) Recognizes and names some plants, animals, their young Identifies the most characteristic seasonal changes in nature Knows several family holidays Interested in new objects, the immediate environment, their purpose , properties. Uses different methods of examining objects, including simple experiments12345Legend:
Manifestation: not formed; is in the formative stage; formed
Note:
ü the indicator “formed” means that the indicator is stable, does not depend on the characteristics of the situation, the presence or absence of an adult, other children, the child’s mood, the success or failure of previous activities, etc.
ü the indicator “is at the stage of formation” means that the indicator periodically appears and its manifestation depends on the characteristics of the situation, the presence of control by an adult, the child’s mood, etc.
ü the indicator “not formed” means that the indicator appears extremely rarely and its appearance is random
Analytical report on the results of pedagogical diagnostics
in the educational field "Cognitive Development"
Target:
— individualization of education for cognitive development (including support for the child, building his educational trajectory of his development);
— optimization of work with a group of children on cognitive development.
Methodology: when conducting pedagogical diagnostics, low-formalized methods were used: observation (in game situations, during regime moments, in directly organized activities)
Diagnostic results: the effectiveness of pedagogical actions was -%, namely:
Formation of elementary mathematical concepts - %. Development of cognitive and research activities - % Familiarization with the subject environment - % Familiarization with the natural world - %
Issues identified:
Causes:
Number of children with special educational needs:
Prospects for optimizing a group of children in terms of cognitive development:
Develop individual educational routes for students:
Last name, first name of the child
INDICATORS / MANIFESTATION Fiction Speech developmentKnows how to listen to works of art, monitors the development of action. With the help of a teacher, he stages and dramatizes short excerpts from folk tales. Reads nursery rhymes and short poems by heart. Shows interest in books. Uses speech to initiate communication. Addresses an adult with requests, questions, shares impressions from personal experience. Answers questions. various questions related to the subject environment Accompanies individual games, drawing, design, everyday activities with speech. Enters into playful interaction with peers using speech Uses all parts of speech, simple common and uncommon sentences with homogeneous members 12345Legend:
Manifestation: not formed; is in the formative stage; formed
Note:
ü the indicator “formed” means that the indicator is stable, does not depend on the characteristics of the situation, the presence or absence of an adult, other children, the child’s mood, the success or failure of previous activities, etc.
ü the indicator “is at the stage of formation” means that the indicator periodically appears and its manifestation depends on the characteristics of the situation, the presence of control by an adult, the child’s mood, etc.
ü the indicator “not formed” means that the indicator appears extremely rarely and its appearance is random
Analytical report on the results of pedagogical diagnostics
in the educational field "Speech development"
Target:
— individualization of education for speech development (including support for the child, building his educational trajectory of his development);
— optimization of work with a group of children on speech development.
Methodology: when conducting pedagogical diagnostics, low-formalized methods were used: observation (in game situations, during regime moments, in directly organized activities)
Diagnostic results: the effectiveness of pedagogical actions was -%, namely:
Fiction - %. Speech development - %
Issues identified:
Causes:
Number of children with special educational needs:
Prospects for optimizing a group of children in speech development:
Develop individual educational routes for students:
PEDAGOGICAL DIAGNOSTICS
level of preschool education
according to the PROGRAM “From birth to school”
Junior group
1Next ⇒
Single-post wooden support and methods for strengthening corner supports: Overhead line supports are structures designed to support wires at the required height above the ground, water...
Mobile electrified feed dispenser: diagram and process of operation of the device...
Papillary patterns of the fingers are a marker of athletic ability: dermatoglyphic signs are formed at 3-5 months of pregnancy and do not change throughout life...
Transverse profiles of embankments and coastal strips: In urban areas, bank protection is designed taking into account technical and economic requirements, but special importance is given to aesthetic...
© cyberpedia.su 2017-2020 — Not the author of the materials. The exclusive right is reserved by the author of the text. If you do not want this material to appear on our site, please follow the link: Copyright Infringement. We will help you write your work!0.007 s.
Health-saving technologies in the pedagogical process of preschool educational institutions
Health
– the state of physical and social well-being of a person (according to the Charter of the World Health Organization).
The health-saving
pedagogical process of a preschool educational institution
- in the broad sense of the word - is the process of raising and teaching preschool children in a health-saving and health-enriching mode; a process aimed at ensuring the physical, mental and social well-being of the child. Health preservation and health enrichment are the most important conditions for organizing the pedagogical process in a preschool educational institution.
In a narrower sense of the word, it is a specially organized interaction between children and teachers that develops over time and within a certain educational system, aimed at achieving the goals of health conservation and health enrichment in the course of education, upbringing and training.
Technology
– is an instrument of professional activity of a teacher, accordingly characterized by the qualitative adjective pedagogical. The essence of pedagogical technology is that it has a pronounced staged nature, includes a set of certain professional actions at each stage, allowing the teacher, even in the design process, to foresee the intermediate and final results of his own professional and pedagogical activities. Pedagogical technology is distinguished by: specificity and clarity of goals and objectives; presence of stages: primary diagnosis; selection of content, forms, methods and techniques for its implementation; using a set of means in a certain logic with the organization of intermediate diagnostics of achieving the goal, criteria-based assessment of results.
The most important characteristic of educational technology is its reproducibility. Any educational technology should be health-saving!
“Health-saving technology” is a system of measures that includes the interrelation and interaction of all factors of the educational environment aimed at preserving the health of a child at all stages of his learning and development. The concept of preschool education provides for not only the preservation, but also the active formation of a healthy lifestyle and the health of pupils.
Health-saving technologies in preschool education are technologies aimed at solving the priority task of modern preschool education - the task of preserving, maintaining and enriching the health of the subjects of the pedagogical process in kindergarten: children, teachers and parents.
The purpose of health-saving technologies in preschool education in relation to a child
– ensuring a high level of real health of a kindergarten pupil and fostering valeological culture, as the totality of a child’s conscious attitude to human health and life, knowledge about health and the ability to protect, support and protect it, valeological competence, allowing a preschooler to independently and effectively solve the problems of a healthy lifestyle and safe behavior, tasks related to the provision of basic medical, psychological self-help and assistance. In relation to adults - promoting the establishment of a culture of health, including a culture of professional health for preschool teachers and valeological education of parents.
PEDAGOGICAL DIAGNOSTICS “PHYSICAL DEVELOPMENT”. PREPARATORY GROUP. GEF DO
Date: October 5-16, 2016
| No. | Last name, first name of the child | INDICATORS / MANIFESTATION | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical Culture | Formation of initial ideas about a healthy lifestyle | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Performs all types of basic movements correctly (walking, running, jumping, throwing, climbing) | Performs physical exercises from different starting positions clearly and rhythmically, at a given pace, to music, according to verbal instructions | Participates in games with sports elements | Performs a jump onto a soft surface from a height of up to 40 cm | Long jumps from a standing position of at least 100 cm | Long jumps from a run up to 180 cm | Jumps in height from a running start to a height of at least 50cm | Jumps over a short and long rope in different ways | Run 30 m, (min. and sec.) | Run 90 m (min. and sec.) | Get up to squat in 30 seconds | Throws a medicine ball (1kg) into the distance | Throws objects at a target from different positions | Hit vertical and horizontal targets from a distance of 4-5 m | Throws objects with the right and left hands at a distance of 5-12 m | Throws objects at a moving target | Able to change formation in 3-4 columns, in 2-3 circles while moving, in 2 ranks after planning for the first or second, maintains intervals while moving | Can ensure correct posture | Applies personal hygiene skills (performs consciously and independently) | Applies cultural and hygienic skills (can monitor one’s appearance, etc.) | Ideas about a healthy lifestyle have been formed | ||
| 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 9 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 10 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 11 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 12 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 13 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 14 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 15 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 16 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 17 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 18 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 19 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 20 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 21 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 22 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 23 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 24 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 25 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 26 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 27 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 28 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 29 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Efficiency of pedagogical influences % | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Legend:
Manifestation: not formed; is in the formative stage; formed
Note:
ü the indicator “formed” means that the indicator is stable, does not depend on the characteristics of the situation, the presence or absence of an adult, other children, the child’s mood, the success or failure of previous activities, etc.
ü the indicator “is at the stage of formation” means that the indicator periodically appears and its manifestation depends on the characteristics of the situation, the presence of control by an adult, the child’s mood, etc.
ü the indicator “not formed” means that the indicator appears extremely rarely and its appearance is random
Analytical report on the results of pedagogical diagnostics
in the educational field "Physical development"
Target:
— individualization of education for physical development (including support for the child, building his educational trajectory of his development);
— optimization of work with a group of children on physical development.
Methodology: when conducting pedagogical diagnostics, low-formalized methods were used: observation (in game situations, during regime moments, in directly organized activities)
Diagnostic results: the effectiveness of pedagogical actions was %, namely:
Physical Culture- %;
Formation of initial ideas about a healthy lifestyle - %.
Issues identified:
Causes:
Number of children with special educational needs:
Prospects for optimizing the physical development group:
Develop individual educational routes for the physical development of pupils:
PEDAGOGICAL DIAGNOSTICS “SOCIO-COMMUNICATIVE DEVELOPMENT” PREPARATORY GROUP. GEF DO
Date: October 5-16, 2016
| No. | Last name, first name of the child | INDICATORS / MANIFESTATION | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Child in family and community | Socialization, development of communication, moral education | Labor education | Forming the foundations of security | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Has an idea of how a person’s position changes with age | The qualities characteristic of their gender are developed in boys and girls | Knows home address and telephone number, first and middle names of parents, their professions | Takes all possible participation in the life of the preschool institution | Takes part in project activities | Complies with the rules of organized behavior in everyday life | Complies with the rules of organized behavior on the street | Complies with the rules of organized behavior in public places | Complies with the rules of organized behavior in public places | In didactic games, negotiates with peers about the order of moves, the choice of cards, schemes | Independently chooses or invents a variety of game plots | Sticks to the intended plan while playing, leaving room for improvisation | Finds a new interpretation of the role and performs it | Models the subject-game environment necessary for the game | Develops the plot over a long period of time (several days, weeks) | Shows himself to be a tolerant and friendly partner | In communication, he expresses his point of view and treats the opinions of others with respect. | Regulates his behavior based on the norms and rules he has learned and accepted in society | The behavior of a boy/girl in most cases corresponds to the traditional idea of the behavior of a man/woman | Strives to follow a positive example | Capable of establishing stable contacts with peers | In joint games, he controls the implementation of the rules and is able to develop the plot of the game with minimal use of toys. | Can independently care for clothes and eliminate disorder in their appearance | Monitors the state of his workspace before and after classes | Responsibly performs duty duties | Shows diligence at work | Brings what he starts to completion | Follows the rules of organized behavior on the road | Possesses emergency behavior skills | Possesses environmentally friendly behavior skills | ||
| 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 8 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 9 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 10 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 11 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 12 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 13 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 14 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 15 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 16 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 17 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 18 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 19 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 20 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 21 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 22 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 23 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 24 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 25 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 26 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 27 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 28 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 29 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Efficiency of pedagogical influences % | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Legend:
Manifestation: not formed; is in the formative stage; formed
Note:
ü the indicator “formed” means that the indicator is stable, does not depend on the characteristics of the situation, the presence or absence of an adult, other children, the child’s mood, the success or failure of previous activities, etc.
ü the indicator “is at the stage of formation” means that the indicator periodically appears and its manifestation depends on the characteristics of the situation, the presence of control by an adult, the child’s mood, etc.
ü the indicator “not formed” means that the indicator appears extremely rarely and its appearance is random
Analytical report on the results of pedagogical diagnostics
in the educational field “Social and communicative development”
Target:
— individualization of education for social and communicative development (including support for the child, building his educational trajectory of his development);
— optimization of work with a group of children on social and communicative development.
Methodology: when conducting pedagogical diagnostics, low-formalized methods were used: observation (in game situations, during regime moments, in directly organized activities)
Diagnostic results: the effectiveness of pedagogical actions was %, namely:
Socialization, development of communication, moral education – %. Child in the family and community - % Self-care, independence, labor education - % Formation of the foundations of safety - % Identified problems :
Causes:
Number of children with special educational needs:
Prospects for optimizing a group of children in terms of social and communicative development:
PEDAGOGICAL DIAGNOSTICS “ARTISTIC AND AESTHETIC DEVELOPMENT”. PREPARATORY GROUP. GEF DO
Date: October 5-16, 2016
| No. | Last name, first name of the child | INDICATORS / MANIFESTATION | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Introduction to the arts | Visual activities | Constructive modeling activities | Musical activities | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Distinguishes between types of fine arts, names the main visual means | Developed artistic perception of works of art | Creates individual and collective drawings, decorative, subject and plot compositions on themes of the surrounding life, literary works | Uses various materials and methods of creating images | Sculpts various objects, creates decorative compositions in various ways | Paints sculpted items based on folk art | Creates plot and decorative compositions, creates images using various methods of cutting and tearing paper of various textures | Able to design objects taking into account their functional purpose | Creates design options for the same object according to 2-3 conditions | Creates different designs from paper | Creates various images from natural materials with taking into account its texture, color and shape | Creates and plays out a design united by a common theme (team work) | Can talk about a piece of music he listened to, express his opinion, compare it with another | Hears the development of a musical image in a work | Names favorite works and their authors | Sings without tension, easily, loudly, expressively | Correctly conveys the melody in songs with musical accompaniment | Sings solo and in choir | Performs movements in dances, exercises, games rhythmically, musically and expressively | Participates in the creation of creative sketches | Plays solo and in an orchestra, performs simple melodies on high-pitched children's musical instruments, improvises | Actively participates in musical performances of songs, comes up with his own variations of movements in games and round dances. Shows creativity by participating in musical dramatization games and theatrical games | Recognizes the National Anthem of the Russian Federation. Anthem of Tula | ||
| 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 9 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 10 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 11 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 12 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 13 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 14 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 15 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 16 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 17 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 18 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 19 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 20 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 21 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 22 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 23 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 24 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 25 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 26 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 27 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 28 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 29 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Efficiency of pedagogical influences % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Legend:
Manifestation: not formed; is in the formative stage; formed
Note:
ü the indicator “formed” means that the indicator is stable, does not depend on the characteristics of the situation, the presence or absence of an adult, other children, the child’s mood, the success or failure of previous activities, etc.
ü the indicator “is at the stage of formation” means that the indicator periodically appears and its manifestation depends on the characteristics of the situation, the presence of control by an adult, the child’s mood, etc.
ü the indicator “not formed” means that the indicator appears extremely rarely and its appearance is random
Analytical report on the results of pedagogical diagnostics
in the educational field "Artistic and Aesthetic Development"
Target:
— individualization of education for artistic and aesthetic development (including support for the child, building his educational trajectory of his development);
— optimization of work with a group of children on artistic and aesthetic development.
Methodology: when conducting pedagogical diagnostics, low-formalized methods were used: observation (in game situations, during regime moments, in directly organized activities)
Diagnostic results: the effectiveness of pedagogical actions was %, namely:
Introduction to art - %. Visual activity - % Constructive-model activity - % Musical activity - % Identified problems :
Causes:
Number of children with special educational needs:
Prospects for optimizing the group for artistic and aesthetic development:
Develop individual educational routes for students
PEDAGOGICAL DIAGNOSTICS “COGNITIVE DEVELOPMENT”. PREPARATORY GROUP. GEF DO
Date: October 5-16, 2016
| No. | Last name, first name of the child | INDICATORS / MANIFESTATION | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Formation of elementary mathematical concepts | Development of cognitive and research activities | Subject environment | Social world | Natural world | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Independently combines various groups of objects that have a common feature into a single set, removes its individual parts from the set, establishes connections and relationships between the whole and the set and its various parts, finds parts of the whole set and the whole from known parts | Counts to 10 and beyond (quantitative and ordinal counting within 20) | Correlates the number (0-9) and the number of objects | Composes and solves one-step addition and subtraction problems | Distinguishes between quantities: length (width, height), volume (capacity), mass (weight of an object), and methods of measuring them | Measures and compares lengths and volumes | Able to divide an object/figure into equal parts, compare the whole and the part | Distinguishes and names: segment, angle, circle, oval, polygon, ball, cube, compares them | Has an understanding of time relationships day/week/month, determines time by clock | Knows the composition of the first ten numbers | Able to obtain each number by adding/subtracting one | Orients himself in the surrounding space and on a plane, indicates the relative position and direction of movement of objects, uses symbolic notations | Knows generalized methods of studying objects using a system of sensory standards and perceptual actions | Acts independently in accordance with the proposed algorithm | Fine motor skills of the hands are developed in a variety of activities. | Takes an active part in all types of projects | Pays attention to analyzing the effectiveness of information sources | Has ideas and some signs of objects in the surrounding world | Selects and groups objects according to cognitive task | Knows about his family | Has an idea of the immediate social environment (kindergarten, school and library, etc.) | Knows the coat of arms, flag, Anthem of Russia, names the main city of the country, has an idea about his native land and its attractions | Knows family holidays and traditions, some public holidays | Knows some representatives of the animal world (animals, birds, etc.) and has ideas about their interaction with humans | Knows the characteristic signs of the seasons and correlates with each season the characteristics of the lives of people, animals, and plants | Knows the rules of behavior in nature and follows them | Establishes elementary cause-and-effect relationships between natural phenomena | ||
| 1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 7 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 9 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 10 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 11 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 12 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 13 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 14 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 15 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 16 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 17 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 18 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 19 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 20 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 21 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 22 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 23 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 24 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 25 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 26 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 27 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 28 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 29 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Efficiency of pedagogical influences % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Legend:
Manifestation: not formed; is in the formative stage; formed
Note:
ü the indicator “formed” means that the indicator is stable, does not depend on the characteristics of the situation, the presence or absence of an adult, other children, the child’s mood, the success or failure of previous activities, etc.
ü the indicator “is at the stage of formation” means that the indicator periodically appears and its manifestation depends on the characteristics of the situation, the presence of control by an adult, the child’s mood, etc.
ü the indicator “not formed” means that the indicator appears extremely rarely and its appearance is random
Analytical report on the results of pedagogical diagnostics
in the educational field "Cognitive Development"
Target:
— individualization of education for cognitive development (including support for the child, building his educational trajectory of his development);
— optimization of work with a group of children on cognitive development.
Methodology: when conducting pedagogical diagnostics, low-formalized methods were used: observation (in game situations, during regime moments, in directly organized activities)
Diagnostic results: the effectiveness of pedagogical actions was %, namely:
Formation of elementary mathematical concepts - %. Development of cognitive and research activities - %
Familiarization with the subject environment
Familiarization with the social environment – % Familiarization with the natural world – %
Issues identified:
Causes:
Number of children with special educational needs:
Prospects for optimizing a group of children in terms of cognitive development:
Develop individual educational routes for students:
PEDAGOGICAL DIAGNOSTICS “SPEECH DEVELOPMENT”. PREPARATION GROUP. GEF DO
Date: October 5-16, 2016
| No. | Last name, first name of the child | INDICATORS / MANIFESTATION | ||||||||||
| Speech development | Fiction | |||||||||||
| Through speech, he takes initiative in communicating with teachers, institution staff, parents of other children, supports the topic of conversation that arises on the initiative of an adult, answers questions and responds to requests, talks on various topics (everyday, social, educational, personal, etc.) | Uses synonyms, antonyms, and complex sentences of various types in speech | Retells and acts out small literary works with the help of dramatization, composes stories about the subject according to a plan and model, according to a plot picture, a set of pictures with a plot development of the action | Distinguishes between the concepts of “sound”, “syllable”, “word”, “sentence” | Names words in a sentence, sounds and syllables in words in sequence | Finds words in a sentence with a given sound, determines the place of the sound in the word | Recognizes works, names 2-3 authors, names favorite books, sets out their content, including large works (in a conversation with a teacher, or based on a book) | Likes to listen to new fairy tales, stories, poems, prefers reading, participates in discussions, expresses his point of view | Looks at illustrated publications with interest, names 2-3 illustrators | Reads poetry expressively, retells excerpts from works | Distinguishes the genre of the work | ||
| 1 | ||||||||||||
| 2 | ||||||||||||
| 3 | ||||||||||||
| 4 | ||||||||||||
| 5 | ||||||||||||
| 6 | ||||||||||||
| 7 | ||||||||||||
| 8 | ||||||||||||
| 9 | ||||||||||||
| 10 | ||||||||||||
| 11 | ||||||||||||
| 12 | ||||||||||||
| 13 | ||||||||||||
| 14 | ||||||||||||
| 15 | ||||||||||||
| 16 | ||||||||||||
| 17 | ||||||||||||
| 18 | ||||||||||||
| 19 | ||||||||||||
| 20 | ||||||||||||
| 21 | ||||||||||||
| 22 | ||||||||||||
| 23 | ||||||||||||
| 24 | ||||||||||||
| 25 | ||||||||||||
| 26 | ||||||||||||
| 27 | ||||||||||||
| 28 | ||||||||||||
| 29 | ||||||||||||
| Efficiency of pedagogical influences % | ||||||||||||
Legend:
Manifestation: not formed; is in the formative stage; formed
Note:
ü the indicator “formed” means that the indicator is stable, does not depend on the characteristics of the situation, the presence or absence of an adult, other children, the child’s mood, the success or failure of previous activities, etc.
ü the indicator “is at the stage of formation” means that the indicator periodically appears and its manifestation depends on the characteristics of the situation, the presence of control by an adult, the child’s mood, etc.
ü the indicator “not formed” means that the indicator appears extremely rarely and its appearance is random
Analytical report on the results of pedagogical diagnostics
in the educational field "Speech development"
Target:
— individualization of education for speech development (including support for the child, building his educational trajectory of his development);
— optimization of work with a group of children on speech development.
Methodology: when conducting pedagogical diagnostics, low-formalized methods were used: observation (in game situations, during regime moments, in directly organized activities)
Diagnostic results: the effectiveness of pedagogical actions was %, namely:
Fiction - %. Speech development - %
Issues identified:
Causes:
Number of children with special educational needs:
Prospects for optimizing a group of children in speech development:
Develop individual educational routes for students: