Cognitive activities
Materials found: 143 Shown: 1 — 10
Integrated educational activity with children of middle preschool age on the topic “Zayushkina’s hut”
Program content. 1. Clarify knowledge about domestic and wild animals. 2. To form an idea of the meanings and functions of a traffic light. Instill traffic rules. 3. Strengthen the ability to determine the length of objects by...
FGT topic Furniture 2 junior group
“Rainbow” - topic “Furniture” Form ideas on the topic “Furniture” 2-ml. group To form an idea of the concept of “furniture”: • purpose; • Types of furniture; • Furniture parts; • What furniture is made from; • Methods of handling. Table,…
Three periods of autumn (compendium)
Summary of direct educational activities on the topic: “Three periods of autumn.” (preparatory group) Educational area “Cognition”: systematize children’s knowledge about autumn and autumn phenomena, consolidate ideas about...
Integrated lesson for children of senior preschool age using TRIZ “Oh, my bast shoes”
Goal: 1. Continue to develop the need for knowledge of the man-made world. 2. Improve knowledge about everyday objects (their color, shape, size, material, purpose. 3. Develop coherent speech. 4. Exercise in…
Summary of an open lesson with children of the preparatory group. NGO "Cognition", "Communication". on Topic: “The Journey of Water”
Lesson notes for the preparatory group Fr. O. “Cognition” “Communication” on the Topic: “The Journey of Water” Form of teaching: open lesson on cognitive and research activities of children. Number of children: subgroup Purpose:…
Summary of direct educational activities. "Autumn Fair"
Goals: to generate interest in the fair. Objectives: To summarize and systematize ideas about autumn according to the main, essential features, to consolidate knowledge about a person’s autumn preparations for winter in the garden. Activating the dictionary for...
Corrective lesson on the topic Clothes
Correctional lesson on the topic Clothes Goal: To develop the ability to differentiate clothes by season, to practice the use of pronouns, to use plural nouns in the nominative case in speech, to develop...
An educational activity with elements of work activity. “A hut is not red in its corners, but red in its pies”
Cognitive lesson with elements of work activity in the senior group. “A hut is not red in its corners - it is red in its pies” Goal: To introduce children to ancient household items and their purpose. Give children knowledge about what yeast is and...
Cognitive-speech lesson in the second junior group. "What grew in the garden"
Municipal budgetary preschool educational institution, child development center - kindergarten No. 19 “Joy” Cognitive - speech lesson in the second junior group TOPIC: “What grew in the garden” Prepared by: Marina Efimova...
Topic: “Journey to the Homeland of the Tomato”
Lushnikova M. V., teacher of the 2nd qualification category of the MKDOU D/s “Cherry”, Vargashi village.
Topic: “Journey to the homeland of the tomato.” Software tasks. Educational: to give children an idea of the plant’s need for light, ... Pages: ...
All sections
Cognitive development in kindergarten
This section of the site contains developments on the cognitive development of children in kindergarten. Cognitive development is a set of quantitative and qualitative changes that occur in cognitive mental processes due to age, under the influence of the environment and the child’s own experience.
Cognitive development involves the cognitive activity of a preschooler. And in order to support cognitive activity, it is necessary to rely on the cognitive interest of children. Cognitive interest is a selective focus on the knowledge of objects, phenomena, events of the surrounding world, activating the mental processes and activities of a person, his cognitive capabilities.
The cognitive development of preschool children is based on cognitive activity, as a result of which the child’s personal experience is formed, his value attitude to the world, and the needs for knowledge and cognition are formed. Through cognitive processes, the child receives and comprehends information. Sensation, perception, thinking, imagination, speech are inseparable parts of a single process of reflecting reality. Sensual visual knowledge of objects and phenomena of the surrounding world creates the initial basis for the formation of the personality of a preschool child.
In the section of the site, cognition, cognitive development in kindergarten contains many interesting activities for educators on teaching children on various topics:
- Educational situation on cognitive and speech development of children in kindergarten
- Open lesson on self-knowledge in a preschool classroom
- Cognition lesson at a preschool educational institution “Let’s Help the Hedgehog”, junior group
- Summary of educational activities with preschool children cognitive development FEMP
- Summary of direct educational activities on cognition, communication and artistic creativity in the senior group “Spring, primroses”
- Summary of direct educational activities educational area “Cognition” on the topic “Water Sorceress” senior group
- Summary of educational activities on cognitive development in kindergarten on the topic “KVN whychek” with children of the preparatory group
- Summary of the open final lesson on cognitive and speech development in the senior group on the topic “Travel with the Sprinkler”
- Summary of educational activities with children in the middle group of kindergarten
- Abstract of GCD in kindergarten cognitive development
- Summary of a lesson on cognitive development in junior group 1
- Summary of organized educational activities in the educational field “Cognitive Development” (FEMP)
- Notes in kindergarten “My Small Motherland” Educational activities of children in the preparatory group cognitive development
- Summary of educational activities “Wonderful Tree” in the field of cognition for children of the second junior group
- Technological map of organized educational activities for children of the middle group educational area “Cognition” section Ecology topic Electrical appliances
- Abstract of the educational activity “Journey to the world of living nature” Educational area Cognitive development
- Summary of a lesson in kindergarten on cognitive development in the senior group
- Summary of organized educational activities on cognitive development in the senior group for children with mental retardation “On the Seabed”
- Lesson on developing the cognitive sphere and creative abilities of older children with mental retardation “Visiting a fairy tale”
- Summary of direct educational activities on cognitive development with children of the preparatory group Russia is my Motherland!
- Cognitive activities in kindergarten
- A feature of a child’s healthy psyche is cognitive activity.
The condition that promotes the development of cognitive activity of pupils is the creation of a favorable psychological microclimate in the children's team, trusting relationships between all participants in the educational process.
One of the most important abilities is the ability to cognition. Cognitive development of children is one of the important areas in working with preschool children. A child is born with an innate cognitive orientation that helps him adapt to new conditions of his life. By the end of his stay in kindergarten, we must help the child master basic concepts in the field of natural science, mathematics, and history. To teach, based on one’s own knowledge, to make independent decisions in different types of activities.
Preschoolers' knowledge of the world occurs mainly through emotional and practical means. Children pay attention to everything unusual, bright, and what they directly encounter. What knowledge about the world should be acquired in preschool age? The surrounding world can be divided into social (people, emotions, relationships), natural (peculiarities of the season, weather phenomena, flora and fauna) and objective (materials and their properties, transformations of objects). Children of primary preschool age (3-4 years old) are mainly interested in objects from their immediate environment, which they can study directly (at home, in kindergarten, on a walk).
A child’s curiosity is constantly aimed at understanding the world around him and building his own picture of this world. The child, while playing, experiments, tries to establish cause-and-effect relationships and dependencies. He himself, for example, can find out which objects will sink and which will float. He has many questions about the phenomena of life around him. The more mentally active a child is, the more questions he asks and the more varied these questions are.
Thanks to the subject Self-Knowledge, which is taught in kindergarten, it makes it possible to more fully solve the problems of the consistent formation of a child’s personality, to reveal and enrich his inner world, and to carry out corrective knowledge of himself and another person.
Design of a cognitive zone in a kindergarten. In the younger group, the children's area is designed taking into account safety rules. When performing active movements, babies lack the coordination of the child. Formation of actions aimed at understanding the surrounding world, development of conscious activity. Development of creative abilities and imagination.
To do this, kindergarten uses all kinds of entertaining tasks, experimental activities, observation, encourages learning through didactic games, etc. Children take a personal part in all these processes, which gives the best result. Methods of cognitive development in preschool educational institutions make it possible to improve such important areas for a child as curiosity, thinking, imagination, memory, logic, and speech.
Through cognitive processes, the child receives and comprehends information. Sensation, perception, thinking, imagination, speech are inseparable parts of a single process of reflecting reality. Sensual visual knowledge of objects and phenomena of the surrounding world creates the initial basis for the formation of the personality of a preschool child.
How to choose an online platform
There are many points that we recommend paying attention to when choosing online classes for comprehensive training:
- How old is the child?
- What are his strengths and weaknesses?
- What does he excel at and what are his leading abilities?
- What is the best time to study?
- Is the site safe?
- How much is it?
In our rating, we tried to take into account all of the above aspects. Let us immediately note that none of the listed sites spam advertisements or offer malicious external links, which ensures complete safety for children.
LEARNING MATHEMATICS
The first thing that comes to mind here is numeracy skills. Because it is still difficult for a child to master calculations. How to teach a preschooler to count?
A child can understand how a specific number relates to the designated number, for example, using counting sticks or cards that depict the number and various objects in the corresponding quantity.
To reinforce counting in order, you can use coloring pages that require you to connect numbered dots.
Also, the consolidation of ordinal counting is facilitated by the constant recounting of surrounding objects: houses, benches, birds, steps on the stairs, apples in a vase.
Mathematics is also geometry. By this age, the child should already know basic geometric shapes. Now it is important to consolidate this knowledge, as well as develop the preschooler’s thinking by playing interesting games with figures. For example, you can fold triangles into rectangles, squares, rhombuses, and other triangles. You can make rectangles from squares.
It is also interesting for children at this age to draw using geometric shapes (everyone knows that a triangle is a skirt, a circle is a sun, a triangle with a rectangle is a house). Also, the child can already compare figures by color, shape, size.
Brief overview of platforms
To make it easier for you to understand, we have selected platforms according to age:
- Online services with game elements and entertainment content for children from 2 years old, 4-5 years old. They are mainly aimed at developing their horizons, getting to know the world around them and the world of letters and numbers.
- Educational sites with numerous tasks for the development of all thinking skills and erudition for preschoolers and primary school children (5-6 and 7-9 years old).
- Educational services for children 10-11 years old with a variety of online simulators, thematic courses and exercises.
MUSICALITY, SENSORY, MOVEMENT
One of the main factors in the proper development of a preschooler at this age remains movement. He must move a lot. This increases his agility, endurance, coordination, develops muscles, and strengthens the skeleton. Therefore, the lesson program should have a lot of space for gymnastics, dancing, exercises, cycling, and all kinds of outdoor games. You can enroll your preschooler in some sports section.
And if motor activity is accompanied by well-chosen melodies, the child will also receive musical development. He will have an improved sense of rhythm, perception of fast and slow music, sad and cheerful.
Advice
At this age, a preschooler can be given to listen not only to children's melodies, but also to classical ones. He already has his favorite tunes, to which he begins to dance or hum.
Sensory perception is, first of all, the development of tactile sensitivity. The baby should have the opportunity to touch a variety of materials and textures: soft, hard, smooth, rough, fluffy, prickly, warm, cold. A good game is to recognize objects by touch without seeing them (for example, by taking them out of a bag).
Improving fine motor skills plays an important role. This helps improve all mental abilities: thinking, speech, memory. In addition, good fine motor skills prepare the hand for writing: the child will hold the pen correctly, the hand will strain and get tired less. Games with small objects and materials are good for this purpose: cubes, construction sets, mosaics, sand, cereals. This also includes finger games, tying shoelaces, fastening zippers, unscrewing corks, drawing, appliqués, and modeling.
Summary of a lesson on the development of cognitive abilities in children 5 - 7 years old.
Being ready for school today does not mean being able to read, write and count.
Being ready for school means being ready to learn it all.
L. A. Wenger, A. L. Wenger
This lesson is aimed at developing in a preschooler such qualities as attention, memory, thinking, and motor development, which are so necessary for entering school.
Lesson: Development of cognitive abilities in children 5-6 years old.
Topic: Let's help the doll Aisulu.
Program content: Continue to teach children to determine the sequence of events; group objects according to common characteristics; develop attention, memory, thinking, fine motor skills, the ability to work according to the proposed model; develop the ability to work in pairs;
Equipment : demonstration pictures from the series “What’s extra” and “What’s first - what’s next”, cards for individual work “Arrange the icons”, “Find the differences”, “Complete the cells”.
Progress of the lesson:
1.Organizational point:
Hello guys! Let's welcome each other to our lesson.
Hello, golden sun!
Hello, blue sky!
Hello my friends,
I'm very glad to see you!
Guys, today the doll Aisulu came to our lesson. She asks for help to complete some tasks, it is very difficult for her to cope with them, because she does not study at school. Shall we help Aisul? (Children's answers)
2. Main part.
Exercise “Say it in one word.” Guys, we need to help Aisul name objects in one word:
A) Oranges, pears, apples, bananas, tangerines are ... (fruits)
B) Tomato, cucumber, carrot, onion, zucchini are... (vegetables)
B) Spruce, poplar, birch, aspen, oak are... (trees)
D) May, November, December, February, August are... (months)
D) Chanterelle, fly agaric, boletus, russula are... (Mushrooms)
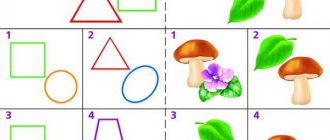
Task “Find the extra object.” You guys are great, Aisulu is pleased with your help. The next task for Aisulu is also very difficult. Let's help her find the extra one among the objects and name it. Children look at the pictures provided, find an extra item, call it: 1) Extra cocktail, because everything else is different types of ice cream; 2) Extra candy, because pie, cheesecake, bagel are baked goods); 3) An extra leaf because the rest are flowers; 4) Extra strawberries, because all the others are mushrooms; 5) There is an extra hedgehog because the rest are pets; 6) An extra cactus, because the rest are African animals; 7) Extra cucumber, and the rest are fruits; 8) There is an extra ball because the rest are vegetables.
How pleased our Aisulu is! And we got ready for the next task.
Exercise "Who is faster." How pleased our Aisulu is! And we got ready for the next task. Take the cards and put icons in the shapes as shown in the example. Let's compete to see who is the fastest. (Children complete the task on cards).
Physical exercise: We clap-clap with our hands, we stomp-stomp with our feet.
We are eyes blink-blink, we are shoulders chick-chick.
One here, two here, turn around.
They sat down and stood up, they sat down and stood up,
Immediately they became Vanka’s stand-up,
And then they started galloping, like our merry ball.
One - two, one - two - the game is over!
Work in pairs “Find the differences”. And now, guys, we will help Aisul find the differences in the pictures. (Children find differences in the pictures).
The game “What comes first, what comes next.” Guys, let's take a close look at the pictures and help Aisul determine what happened first and what happened next.
The task “Complete the drawings in the cells.” Guys, Aisulu has unusual pictures, but they are only half drawn. Let us finish the second half so that the picture is complete. (The guys complete the picture by cells.)
3. Summary of the lesson.
Guys, our lesson is over. You were all great, you all did a great job.
Tell me, did you have any difficulties?
What did you like most about the lesson?
What else would you like to repeat?
Guys, the Aisulu doll was very pleased that you helped her. She has prepared sweet gifts for you.